Cold Formed Purlins and Girts
Cold-formed steel (CFS) sections are increasingly favored in structural systems for their high strength-to-weight ratio, ease of fabrication, and efficient installation. Compared to hot-rolled steel (HRS), cold-formed steel members offer lighter solutions while maintaining practical and reliable structural performance.
In modern industrial, warehouse, and low-rise buildings, cold-formed steel Z and C sections are widely used as secondary specifically as purlins and girts supporting roof and wall cladding.
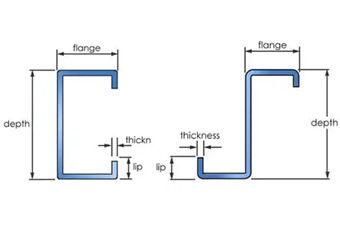
MkaPEB enables users to design building purlins and girts using cold-formed steel sections, resulting in significant weight reductions compared to designs using hot-rolled sections.
When using cold-formed elements, they can instead be designed as continuous beams. This continuous configuration typically results in lower maximum bending moments compared to simply supported spans, enabling the use of lighter and more efficient solutions.
The commonly adopted methods to maintain continuity over the interior support are
- Lapped connection (Z-sections)
- Sleeve connection (C-sections)
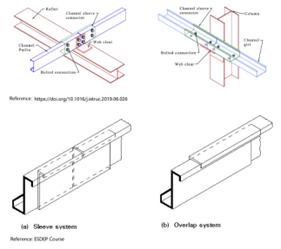
In the case of channel sections with the same cross-sectional dimensions, overlapping is not possible and therefore external sleeve connection is preferred. However, Z sections can simply be overlapped, therefore they are more preferable to be used as purlins and girts to provide continuous purlin/girt systems.
MkaPEB enables users to model lapped connections for Z-sections, allowing for lighter and more efficient building designs.
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Easily create Help documents