Expansion Gaps
Due to thermal effect, typically building dimensions are restricted, or expansion joints are required in the structure when horizontal dimensions exceed certain limits.
Maximum allowable building length without expansion joints is dependent upon many variables, including ambient temperature during construction and the expected temperature range during the lifetime of the building.
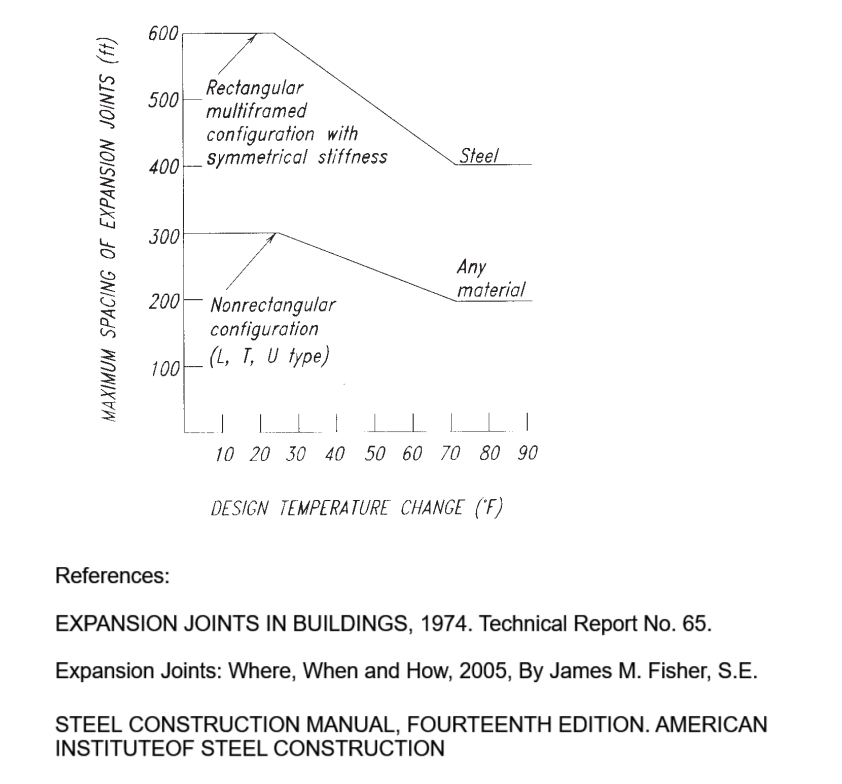
However, other factors affect the maximum allowable building length without expansion joints:
1. If the building will be heated only and will have pinned column bases, use the maximum spacing as specified.
2. If the building will be air-conditioned as well as heated, increase the maximum spacing by 15% provided the environmental control system will run continuously.
3. If the building will be unheated, decrease the maximum spacing by 33%.
4. If the building will have fixed column bases, decrease the maximum spacing by 15%.
5. If the building will have substantially greater stiffness against lateral displacement in one of the plan dimensions, decrease the maximum spacing by 25%.
The growth of steel structures can’t be stopped, but the direction it grows in most definitely can. In the sketches illustrated below, the option 3 bracing system results in a building that minimizes thermal expansion.
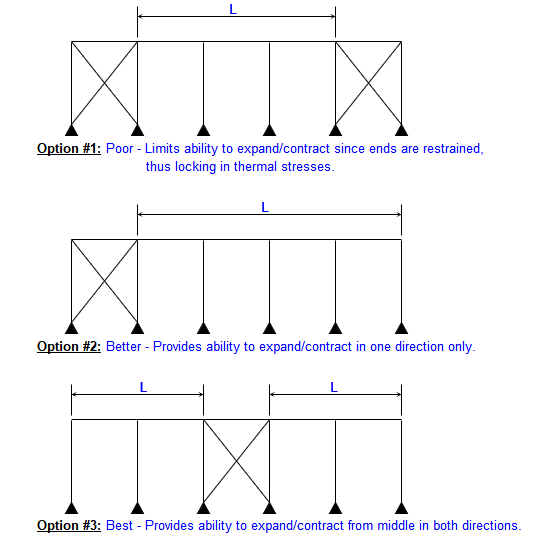
It should be noted that inter-frame bracing at the building ends can restrict thermal expansion, thereby locking in thermal stresses within the structure.
Considering all the above factors MkaPEB calculates the maximum spacing of the expansion joints:
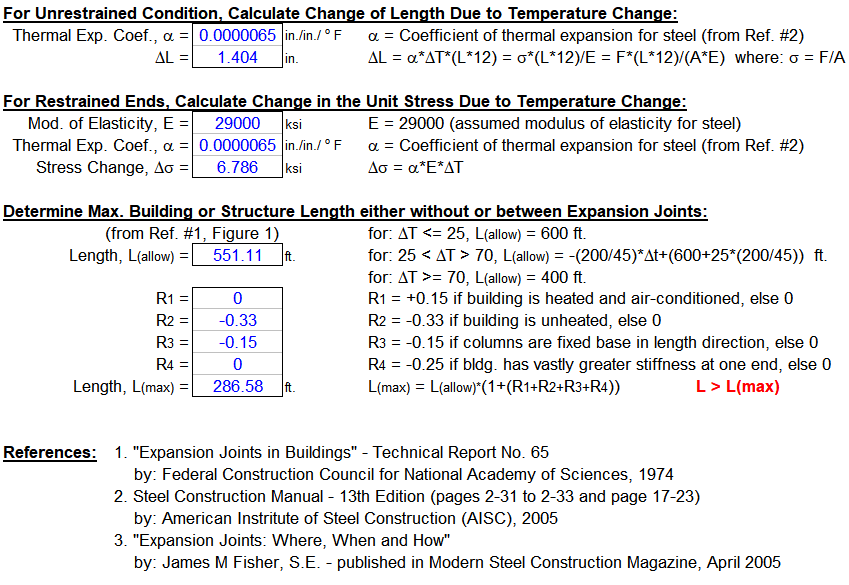
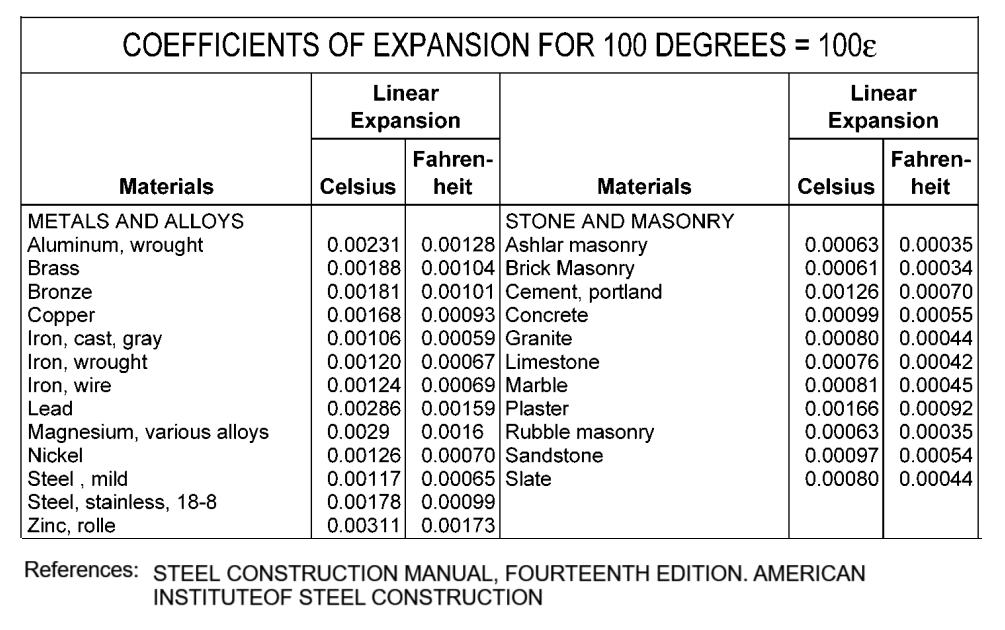
The coefficients of thermal expansion for different materials are obtained from the table below
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Converting Word Docs to eBooks Made Easy with HelpNDoc