Purlins and Girts
Cold-formed steel (CFS) sections are widely used due to the advantages it offers over the hot rolled steel (HRS) such as higher strength to weight ratio, ease of fabrication and installation. CFS sections are commonly used as a secondary member (purlin and girt) in many structures such as industrial buildings, low to medium rise office buildings and warehouses. Typically, cold-formed steel Z and C sections are used as purlins and girt (secondary member) to support the cladding (roof and wall cladding) since these sections are easy to fabricate and erect and are economical as well.
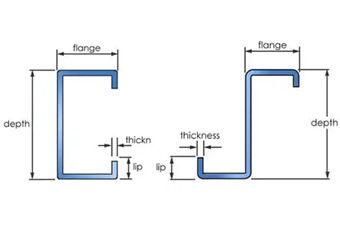
In general, there exists a limitation on the maximum transportable length and hence there is a need to ensure effective redistribution of bending moment at the location of discontinuity. The commonly adopted methods to maintain continuity over the interior support are
- Lapped connection
- Sleeve connection
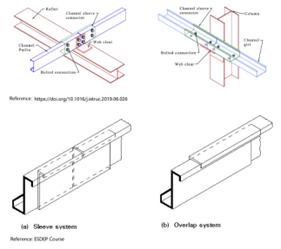
In the case of channel sections with the same cross-sectional dimensions, overlapping is not possible and therefore external sleeve connection is preferred. However, Z sections can simply be overlapped, therefore they are more preferable to be used as purlins and girts to provide continuous purlin/girt systems.
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Easily create Help documents